An allergy occurs when the immune system reacts to foreign substances causing a reaction in many people. These allergies could be due to pollen, certain types of food or even insect stings. Allergies can range in severity from mild to severe, requiring hospitalization. Therefore, it is wise to identify the allergies one has and engage in modern de-sensitisation therapies to overcome the allergy successfully.
In Singapore, the ENT Clinic offers comprehensive care for allergies. The team uses the latest techniques for allergy diagnosis and helps with successfully controlling the allergies though de-sensitisation techniques. This treatment is available for both children and adults.
Table of Contents
What are allergies?
Allergies are brought about when the immune system makes antibodies against a certain type of allergen. Our bodies normally produce antibodies, and when the body comes in contact with substances that it identifies as foreign, then antibodies are produced against these allergens. The response by the body when it comes in contact with the allergens is that it brings about skin inflammation, as well as inflammation of the digestive system, airways and sinuses. The severity of the allergy can range from mild to moderate to severe. Today, allergies can be well controlled through treatment.
What are the symptoms of an allergy?
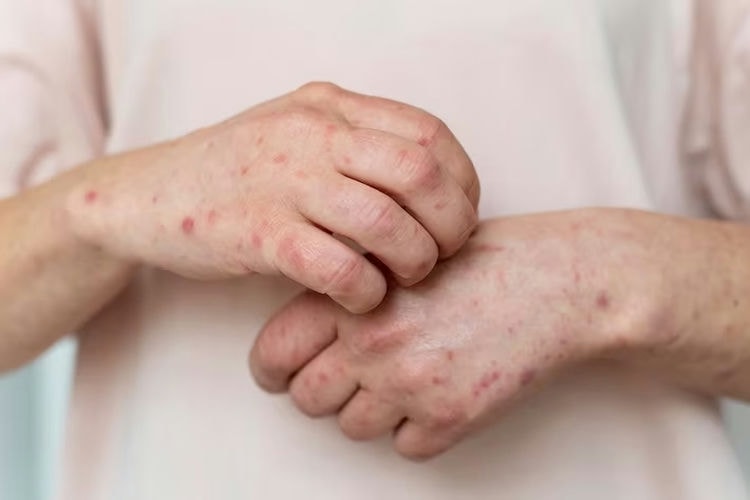
The symptoms of the allergy depend on the allergen involved. Allergies can affect your airways, nasal passages, digestive tract and skin and it can range from mild to very severe conditions.
Food Allergy: Inflammation in the lips, tongue, throat and face
- Tingling sensation in the mouth
- Skin rashes
- Anaphylaxis
Hay Fever: Nasal congestion
- Itchiness in nose, eyes and mouth
- Pink watery eyes
- Runny nose
Drug Allergy: Swelling in face
- Rashes
- Itchy skin
- Hives
- Wheezing
- Anaphylaxis
Insect Allergy: Swelling at the sting site
- Hives on skin
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Anaphylaxis
Atopic dermatitis or eczema: flaky skin
- Redness and itchiness in skin
Anaphylaxis: This is the trigger of a severe reaction due to certain allergens causing a severe life-threatening medical emergency. The observed signs of anaphylaxis causes one to go into shock:
- Hypotension
- Loss of consciousness
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness
- Skin rash
- Nausea
- Weak pulse
Inhalant Allergens: Inhalant allergens or allergens which travel through the air and land on the eyes and nose are quite common which leads to allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis and asthma. Some of the typical allergens are dust mite, grasses, pollen and pet hair. While nasal sprays and antihistamines are used to control symptoms, it might not decrease the underlying inflammation.
What are the risk factors of allergies?
One might run the risk for allergies if there is a family history of allergies or asthma. Having hay fever or hives predisposes to allergy or another allergic condition.
What are the complications of allergies?
Having an allergy could increase the risk of other medical conditions and the complications include:
- Ear infections and sinusitis: The risk of having ear infections, sinusitis and lung conditions are higher with hay fever and related conditions.
- Asthma: Asthma affects breathing and the airways. Generally, when one has allergies, they are more likely to have asthma too. Asthma is triggered due to allergens in the environment.
- Anaphylaxis: Persons who have severe allergies are prone to allergy induced reactions. Anaphylaxis is triggered by foods, medication and insect stings.
How can allergies be prevented?
Preventing allergic reactions depends on the type of allergy you have. General measures include the following:
- Avoiding of the known triggers: This is the best way to avoid an allergy. Even if you are being treated, staying away from pollen or other allergens is helpful. Having the home free of dust and washing linen often is helpful.
- Maintaining a diary: Trying to identify a diary helps to understand which may be worsening or causing an allergy. Tracking activities and having a check on what you eat is helpful to identify the triggers.
- Wearing a medical alert bracelet: Individuals who have severe allergies should wear a medical alert bracelet to let others know if they have a serious allergy. This will act as a way to communicate in case of a reaction.
How is an allergy diagnosed?
An otolaryngologist will have a detailed physical examination and analysis of medical history to understand the condition. It will be helpful to show the detailed diary you are maintaining. Some of the common tests for identifying an allergy include:
- Skin test: The skin will be pricked with small amounts of proteins found in common allergens and if one is allergic to an allergen then a raised red bump would appear.
- Blood Test: This helps to measure the allergy-causing antibodies and it helps to find the sensitivity to allergens. Blood is tested for specific IgE or immunoCAP testing.
What are the treatments for allergies?
Apart from allergy avoidance, some of the other ways to treat allergies include:
- Medications: The ENT specialist will give prescription and non-prescription medications like nasal sprays, eye drops and pills to reduce the immune system reactions to ease symptoms.
- Emergency epinephrine: Persons with severe allergies should consider carrying an emergency epinephrine shot at all times. It is given for severe allergic reactions to help reduce symptoms till emergency treatment is available.
- Immunotherapy or desensitization: This helps persons with severe allergies who are not relieved by usual treatments. It involves a series of injections of purified allergen extracts injected over a period of few years. This treatment is given in small amounts and then gradually increased. Through this treatment, the immune system adjusts gradually and persons become less allergic. It is seen that 85% of people improve with desensitisation and use of medications decreases by over 80%. Treatment involves injections under the skin given subcutaneously or drops under the tongue. Allergy specialists generally give injections weekly for 14 weeks and then give the injections monthly for about 3 years. To gain long lasting benefits it is important to practice the schedule given by the allergy specialist. Generally, this is a permanent therapy for many. Subcutaneous desensitization is generally more significant compared to sublingual drops.
When a patient has allergies and is looking for medical advice, a visit to the ENT Clinic that conducts desensitisation therapy for both adults and children will be a preferred course of action.






